Holoptelea Integrifolia, Vavla, Wawal –
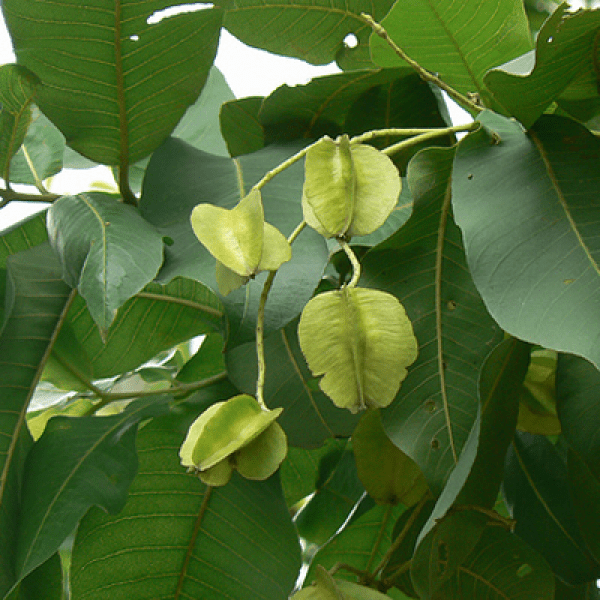
Indian Elm is a large deciduous tree, gowing up to 18 m tall. It has grey bark, covered with blisters, peeling in corky scales on old trees. Alternately arranged leaves are elliptic-ovate, 8-13 cm long and 3.2-6.3 cm wide, smooth, with entire margins, and a pointed tip. Leaf base is rounded or heart-shaped. Stipules are lance-shaped
Common name: Indian Elm, entire-leaved elm tree, jungle cork tree, south Indian elm tree
Color: greenish-yellow to brownish,
Bloom time: Feb- March
Height: 18.00 m
Difficulty level: easy to grow
Planting & Care
plant have long tap roots which need to stretch out so the plants prefer well-dug, loose, well-draining soil; in preparing a bed, dig down 2 feet in depth and about 3 feet across to ensure the soil isn’t too compact.
Sunlight: Full Sun
Soil: well-drained soil
Water: Medium
Fertilizer: Apply any organic fertilizer
Care:
While the plant is small, water around the root zone, about 3 to 4 in.
from the plant.
To protect the plant, it may help to put snail or slug bait around the ste
Special Feature:
Flowers are small, greenish-yellow to brownish, pubescent, borne in short racemes or fascicles at the scars of fallen leaves. Sepals are velvety, often 4. Fruit is an a circular samara, 2.5 cm in diameter, with membranous, net-veined wings, and flat seed.
Use
Medicinal use:
Unverified information The bark of Indian Elm is used in rheumatism.
Seed and paste of stem bark is used in treating ringworm.
Bark and leaves are used for treating oedema, diabetes, leprosy and other skin diseases, intestinal disorders, piles and sprue.
Ornamental use:
The plant is used for ornamental purpose.
Note:
for medicinal use, please consult appropriate doctor before use.
₹499.00
Available on backorder
Available on backorder
Payment Methods:









 EXOTIC PLANTS
EXOTIC PLANTS AIR PURIFIERS
AIR PURIFIERS AQUATICS
AQUATICS AVENUE TREES
AVENUE TREES BAMBOOS
BAMBOOS BONSAI
BONSAI CACTUS
CACTUS CLIMBERS
CLIMBERS CREEPERS
CREEPERS CYCAD
CYCAD FERNS
FERNS FICUS
FICUS FIG
FIG FLOWER PLANTS
FLOWER PLANTS FRUIT PLANTS
FRUIT PLANTS GROUND COVERS
GROUND COVERS HEDGES
HEDGES HERBS
HERBS INDOOR PLANTS
INDOOR PLANTS MEDICINAL PLANTS
MEDICINAL PLANTS ORNAMENTAL PLANTS
ORNAMENTAL PLANTS OUTDOOR PLANTS
OUTDOOR PLANTS PALMS
PALMS SHRUBS
SHRUBS SPICES
SPICES NATURAL
NATURAL CRYSTAL
CRYSTAL ONEX
ONEX PEBBLE CHIPS
PEBBLE CHIPS GLASS & AQUARIUM
GLASS & AQUARIUM GRANITE & MARBLE
GRANITE & MARBLE POLISHED MARBLE MIX CHIPS
POLISHED MARBLE MIX CHIPS POLISHED MIX
POLISHED MIX STONE SAND
STONE SAND UNPOLISHED CHIPS
UNPOLISHED CHIPS SEEDLING GERMINATION TRAYS
SEEDLING GERMINATION TRAYS STAINLESS STEEL PLANTERS
STAINLESS STEEL PLANTERS SYNTHETIC POTS
SYNTHETIC POTS ARTIFICIAL GRASS
ARTIFICIAL GRASS NATURAL GRASS
NATURAL GRASS